Summary:
The RainOff computer program, or simulation
model,
calculates runoff from rainfall on watersheds
(hydrologic catchment areas) whose extension is
limited by the condition that the rainfall can be
assumed evenly distributed over the area.
The program can be freely downloaded, it is free
shareware in the public domain.
The rainfall is converted into recharge by
routing
through a retention reservoir from which water
escapes depending on predetermined characteristcs
as storage capacity, initial storage and maximum
rate of escape (representing evaporation or
subsurface drainage). This first reservoir
gives the recharge
(rainfall excess) as overflow.
The recharge is routed through a second,
non-linear, reservoir with a reaction factor
whose value depends
on the storage level. Thus, the conversion
(transformation) of rain into runoff (surface
drainage) and flooding is produced.
Modelling with RainOff gives the opportunity of
predicting the hydrology of the watershed
(catchmnent) and of flood forecasting as well as
simulating discharge and water table height in
subsurface drainage systems. For the latter case,
the model program offers a calculator to compose
the reservoir reaction factor or response
function from the
characteristics of the system.
|
Details:
The reaction (response) factor can be determined
from recorded rainfall-runoff data. The program
uses various reservoir functions and selects the
optimal function. Alternatively, it is possible
to introduce the reservoir function, together
with rainfall data, and the program will
calculate the runoff.
More details are given in the program itself.
On 12 December 2010 an extra graph was provided
for the recorded rainfall-runoff statistics and
trends, thanks to a suggestion by Mr. Juan
Victoria.
On 27 August 2012 the program was updated to
include a quadratic reservoir function and on
1 december 2012 a Help function and an
observed-calculated graph was added.
On 3 January 2018 the program was given more
versatility by dividing the runoff data into a
high and a low range with different reaction
factors.
|
Start:
The program starts giving clicking on
RainOffT.Exe.
More information is given in the program itself.
|
Documentation:
A description of the procedure and equations used
in RainOff is found in this paper on the
reservoir model.
A lecture note ("Data Analysis") on drainage
research with examples of RainOff applications is
found on the articles
page.
An example of the application of the Curve Number
Method for the design of a surface drainage
system for sugar cane plantations in a humid
tropical coastal area can be found in a chapter
("Agricultural Drainage Criteria"), also on the
articles page.
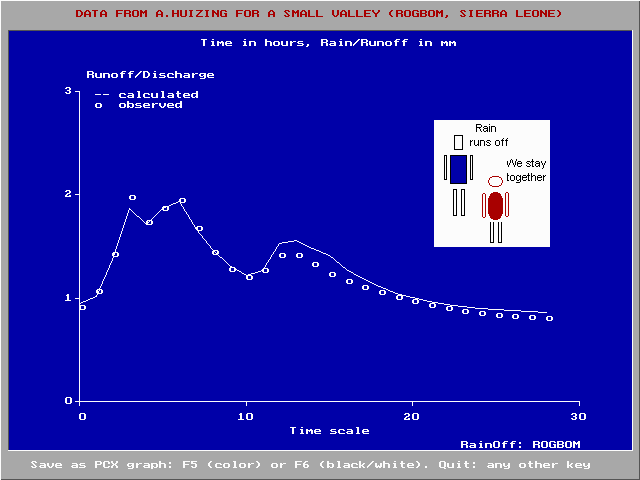
An article on rainfall-runoff relations of a
small valley in Sierra Leone using RainOff with a
non-linear reservoir has appeared in the
International Journal of Environmental Science,
see this website or find it in
this place
The data used in the Sierra Leone articles were
found in this report of
A.Huizing
A comparison of results of the drainage software
EnDrain and RainOff for
steady and non-steady state drainage flow and
water level can be consulted at
ResearchGate or on this
web site
The application of RainOffT is also demonstrated
with the rainfall-runoff data of the
"Herbornseelbach" in Hesse, Germany. Read the
report using
this link.
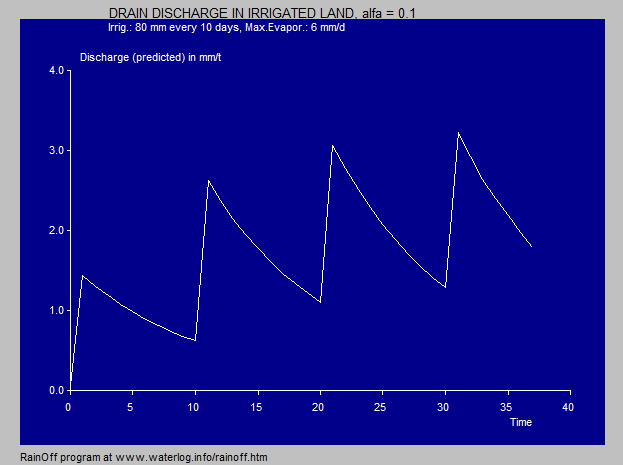
The use of RainOff for the evaluation of the
hydrologic effects of agricultural subsurface
drainage systems can be inspected at this
validation page and at
application.
|
Experiences:
For improvement, I am interested to learn about
your experiences with RainOff. For this there is
a contact form.
|
|
Download
RainOffT
Go to:
Software
& models
General articles
& manuals
Artículos
(in Spanish,
en Español)
Published
reports & cases
Particular
reports & cases
FAQ's
& answers
Home
page
|