THE ENERGY BALANCE OF GROUND WATER FLOW
R.J.Oosterbaan 1), J.Boonstra 1), and K.V.G.K.Rao 2)
1) International Institute for Land Reclamation and
Improvement (ILRI)
P.O. Box 45, 6700 Wageningen, The
Netherlands
2) Central Soil Salinity Research Institute (CSSRI)
Karnal-132001, Haryana, India
Published in: Subsurface-Water Hydrology, p. 153-160
Kluwer Academic publishers, The Netherlands, 1996
On website www.waterlog.info
|
|
ABSTRACT
An energy balance of ground water (groundwater) flow
is introduced. It is based on
equating the change
of hydraulic energy flux over a horizontal distance to
the conversion
rate of hydraulic energy into to friction of flow over
that distance.
The energy flux is calculated on the basis of a
multiplication of the hydraulic potential
with the flow velocity, and is integrated over the
total flow depth. The conversion rate is
determined in analogy to the Joule heat loss equation
of an electric current.
The hydraulic energy balance is applied to the
steady-state flow of water in a phreatic
aquifer recharged by downward percolation stemming
from rainfall or irrigation, and a
quantitative example is given using a numerical
solution.
It is shown that the gradient of the water table is
smaller than that calculated with the
current methods, which do not take into account the
energy associated with the incoming
percolation water.
|
Software
& models
Articles
& manuals
Reports
case studies
FAQ's
& answers
Home
page
Contact
form
|
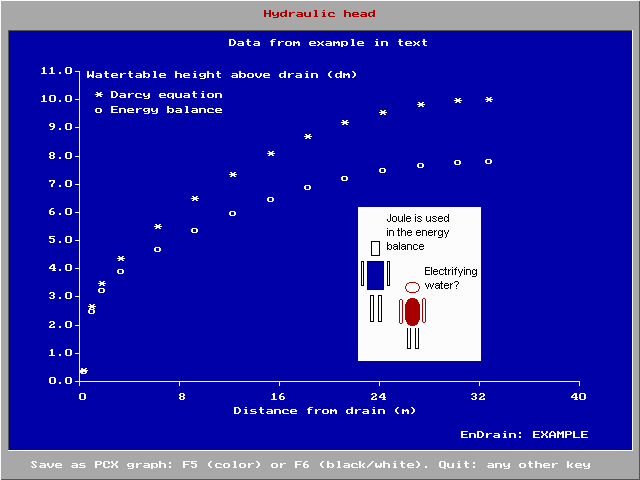
|
Shape of the water table with and without energy
balance
It is calculated that the depth of
the water table diminishes with the
distance from the drains.
The water table is flat midway between the drains
(at half the distance of the drain spacing),
elsewhere it is curved.
With the energy balance equation the water table is
deeper than that calculated with the traditional
Darcy equation.
|
|
