17. AGRICULTURAL DRAINAGE CRITERIA
This article discusses the role of drainage criteria
in the design of agricultural drainage systems. For
this purpose the kinds of drainage systems are
thoroughly analysed and the important design factors
are identified. As the aim of drainage systems is to
enhance crop production, the relations between the
system's parameters and agricultural performance need
to be assessed.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
17.1 Introduction
17.2 Types and Applications of Agricultural Drainage
Systems
17.2.1 Definitions
17.2.2 Classification
17.2.3 Applications
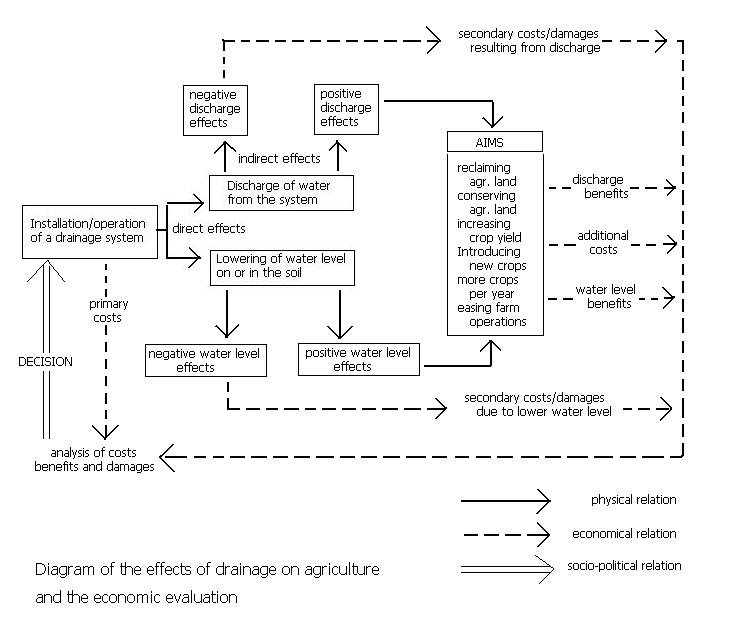
17.3 Analysis of Agricultural Drainage Systems
17.3.1 Objectives and Effects
17.3.2 Agricultural Criterion Factors and Object
Functions
17.3.3 Water table Indices for Drainage Design
17.3.4 Steady-State Versus Unsteady-State Drainage
Equations
17.3.5 Critical Duration, Storage Capacity, and Design
Discharge
17.3.6 Irrigation, Soil Salinity, and Subsurface
Drainage
17.3.7 Summary: Formulation of Agricultural Drainage
Criteria
17.4 Effects of Field Drainage Systems on Agriculture
17.4.1 Field Drainage Systems and Crop Production
17.4.2 Water table and Crop Production
17.4.3 Water table and Soil Conditions
17.4.4 Summary
17.5 Examples of Agricultural Drainage Criteria
17.5.1 Rain-Fed Lands in a Temperate Humid Zone
17.5.2 Irrigated Lands in Arid and Semi-Arid
Regions
17.5.3 Irrigated Lands in Sub-Humid Zones
17.5.4 Rain-Fed Lands in Tropical Humid Zones
References
|
Category
selection:
Software
& models
Articles
& manuals
Reports
case studies
FAQ's
& papers
Home
page
|
|