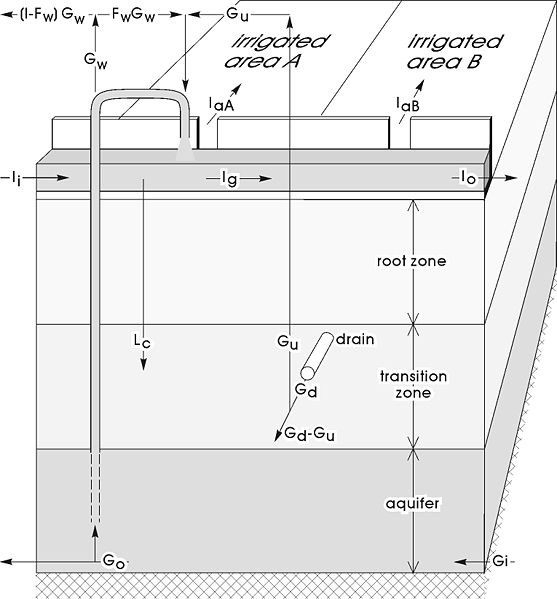
SaltMod calculates water and salt balances including the reuse of groundwater by pumping from wells.
It also calculates the capillary rise from the depth of the water table and the shortage of irrigation water compared to the evaporation.
The subareas with different cropping patterns can influence each other by transport of water through the aquifer.
The soil salinity is derived from the balance of incoming and outgoing salts.
Farmers responses to changing soil conditions can be evoked.